Introducing Chaumian Mints
A Revolutionary Approach to Digital Currencies
In the world of digital currencies, the concept of anonymity has always been an elusive one. While traditional payment systems require the disclosure of sensitive financial information, the rise of cryptocurrencies has brought about a new approach to digital currencies that values privacy and security. However, even cryptocurrencies can sometimes fall short of providing complete anonymity.
This is where Chaumian mints come in. Chaumian mints are digital entities that allow for the issuance of electronic currency or e-cash, which can be used to make anonymous transactions without revealing the identity of the user. The concept of e-cash was introduced by David Chaum in the 1980s, and it has since evolved to become an important part of the digital currency landscape.
So, what exactly is a Chaumian mint? A Chaumian mint is a digital entity that issues digital tokens that can be used for transactions. These tokens are signed by the mint to ensure their authenticity and can be used to make anonymous transactions without revealing the identity of the user. The mint itself serves as a trusted third party, responsible for verifying the validity of the tokens and ensuring that they are not spent more than once.
One of the key features of e-cash is its anonymity, which is achieved through the use of cryptographic protocols and digital signatures. By using digital signatures, Chaumian mints are able to verify the authenticity of digital tokens, while also ensuring that the user's identity is not revealed. This allows for truly anonymous transactions, with no need for users to disclose any personal information.
While the concept of e-cash has been around for decades, it has yet to be widely adopted. This is due in part to the challenges of implementing a system that is both secure and anonymous. However, the principles of e-cash have influenced the development of other digital currencies, including cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Monero.
Bitcoin, for example, provides users with a level of anonymity through the use of pseudonymous addresses, which are not tied to the identity of the user. However, the blockchain itself is a public ledger, which means that all transactions are visible to anyone with access to the network. This has led to the development of other digital currencies, such as Monero, which are designed to provide greater levels of privacy and anonymity.
Monero, like other privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, uses a combination of techniques to achieve anonymity, including ring signatures, stealth addresses, and confidential transactions. Ring signatures allow users to sign a message on behalf of a group, making it impossible to determine which member of the group actually signed the message. Stealth addresses allow users to create unique addresses for each transaction, making it difficult to track the flow of funds. Confidential transactions use a form of encryption to obscure the amount of currency being sent.
While Monero and other privacy-focused cryptocurrencies offer a higher level of anonymity than Bitcoin, they are not without their challenges. For example, because transactions are more complex, they can take longer to process and may require more resources. Additionally, the anonymity provided by these cryptocurrencies can also make them more attractive to criminals, leading to concerns about their use in illegal activities.
Despite these challenges, the concept of Chaumian mints and e-cash has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about digital currencies. By providing a way for users to make truly anonymous transactions, e-cash has the potential to enhance privacy and security in the digital realm. While we may not yet see widespread adoption of e-cash or Chaumian mints, the principles they embody will continue to influence the development of digital currencies for years to come.
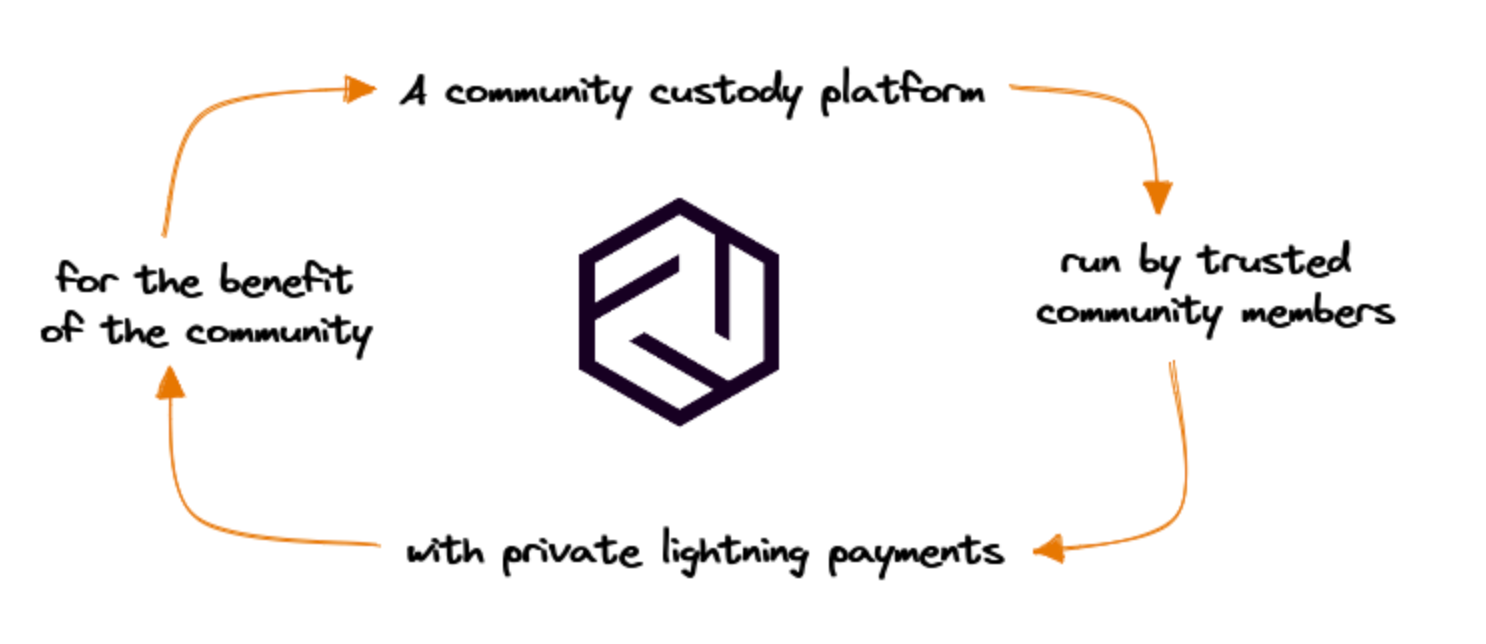
Federated Mints (like Fedimint) have the potential to scale to hundreds of thousands of communities and millions and billions of people. Get informed.